IkamvaYouth is pleased and proud to announce the publication of Against the odds: An evaluation of the IkamvaYouth programme, by a team of economists at the University of Stellenbosch. Servaas van der Berg and his team conducted an in-depth evaluation of IkamvaYouth, by administering questionnaires and interviewing 828 ikamvanites (past and present).
The full report is available here for download, and contains a wealth of information, results, analysis, quotes from ikamvanites and recommendations for improvements and scale.
Some of the findings have validated the results we’ve reported via our own tracking (see below). However, there were also some new and interesting findings, including:
- Insight into ikamvanites’ wealth and living standards
- Only 38% of ikamvanites live with their parents; 45% sometimes go to bed hungry; only 31% have their own desk or table at home and 65% have their own bed.
- 22% of mothers have matric and 11% have some post schooling
- 15% of fathers have matric and 9% have some post schooling; 32% of fathers’ education levels are unknown
- Matric results as compared with those of our feeder schools
- Detail regarding learners’ choosing Maths and Science and their performance in these most-challenging subjects
- “An overwhelming majority (81%) of Ikamva students in 2011 elected to do Mathematics, versus less than half of all candidates nationally. For Physical Science too, far more Ikamvanites chose this difficult option. Reponses to the survey indicate that similarly high proportion of former Ikamva students had elected these two subjects: 78% wrote Mathematics and 54% Physical Science.”
- “The difficulty of these subjects can be gauged from the fact that nationally, the pass rate (at 30%) is 46% and 53% for these two subjects respectively, much lower than for other electives such as Geography (70%) or History (76%), despite the fact that the candidates in these first two subjects are a far more select group in terms of academic ability. This ambitious subject choice is even more exceptional when compared to learners from similar (mainly township) schools. Ikamva’s encouragement of learners to take these more difficult subjects necessarily affects the relative pass rates and the subject performance of Ikamva learners negatively, thus the need to carefully consider this when evaluating Ikamva learners’ results.”
- “61% of all Ikamva matric candidates wrote and passed Mathematics, as against only 21% for all South African matric candidates.3 The proportion of all Ikamva matric candidates who achieved 40% or more was 28% versus 14% for all South African candidates. Compared to similar communities the Ikamva performance in this regard would even be more impressive than this.”
- ” What Ikamva thus successfully manages to do is to encourage learners from across the ability spectrum to raise the bar, by entering for subjects which the typical student from weak schools would usually avoid, and then to achieve success which is at least comparable to that achieved by candidates that often are more selected in terms of ability and from higher socio-economic groups. This is a truly impressive achievement.”
- The good results are consistent: “average results differ little between branches”
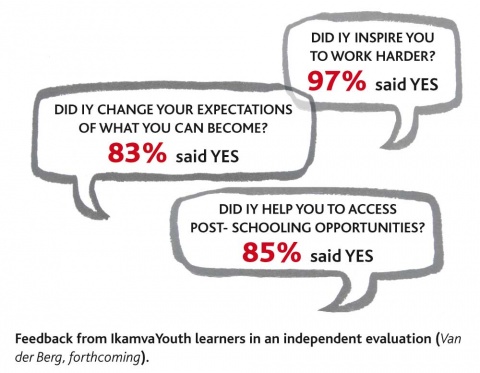
- The programme is very highly regarded by our learners and ex-learners (they do tell us these things, but it means a great deal more when told to independent evaluators)
- “The evaluation team is confident that Ikamva’s short term impact is considerable. This lies not only in the improved matric performance, but even before that in helping to create an environment where children from often very disadvantaged circumstances feel a sense of belonging and that someone cares about their needs and ambitions. That alone is a very valuable contribution. The extent of this contribution cannot be measured, but is visible in the fact that Ikamva was so highly praised by all who participates in it, or have done so in the past. As an evaluation team we have not seen such universally high praise of an organisation before.”
- Insight into the “success factors” behind the IY model
- “The remarkably successful personal relationships that Ikamva has developed with participants, based on extremely sensitive interaction with learners, yet without undermining basic discipline: “Kickouts” still occur and learners know that they can only remain part of the “family” if they play their part.”
- The tutors: “They are largely volunteers and mostly young. The fact that many of them are former Ikamvanites say something about the glue that holds Ikamva together: A positive social context in an environment where many face harsh circumstances at home, in the labour market, schools, universities, and wider society. The link with Ikamva means much to them, and also provides some continuity in their lives. Also, they act as role models to learners, thus further strengthening the desire of learners to undertake tertiary studies. Their relative youth also means that communication with learners is easier, in contrast to what learners experience at school. The team found no evidence that the tutors were particularly well trained or that they were always much better teachers than those in schools; the commitment, positive interaction and additional time were apparently most important in the success of students, not the better teaching.”
- “The fact that Ikamva operates in metropolitan environments where there are universities close by is an important factor in its success. Without a strong volunteer base, the tutors would not have been available, and it would have been more difficult to build the passion for tertiary studies that drives many Ikamvanites.”
- “The most important factors in Ikamva’s success, however, appear to be its commendable organisation, good planning and the enthusiasm of those at the head of the organisation. This enthusiasm is contagious.”
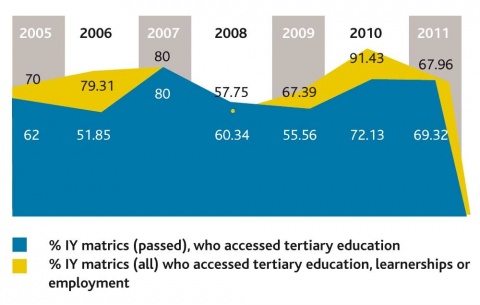
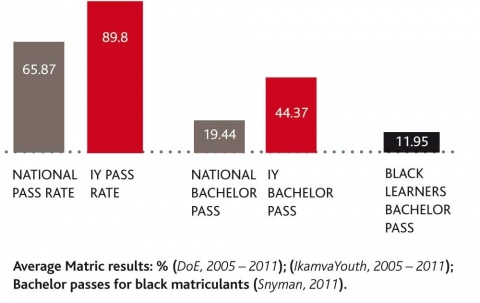
- Matric results
- “85% of Ikamva candidates passed, against the 70% nationally, or put differently, that Ikamva’s failure rate of 15% was half of the national average. But the full extent of Ikamva’s performance success is not yet captured in simple pass or fail rates: What is quite impressive is Ikamva’s performance in terms of getting learners access to universities: 36% of Ikamva candidates, versus 24% nationally, obtained a so-called “Bachelor’s degree endorsement”, i.e. a pass that is considered by the Department of Basic Education as good enough for degree studies. This is what used to be referred to in the past as “university exemption”. Data on a race basis is not yet available for 2011, but to put the Ikamva performance in terms of potential university entry in perspective, it is worth considering that the proportion of black students who obtained such exemptions in 2007, the last year for which race data could be obtained, was only around 11%. Altogether 72% of Ikamva candidates passed with either Bachelor’s or a Diploma endorsement, i.e. could potentially attend a university for degree or diploma studies (some universities have stricter entry criteria, though), whilst this proportion is only 53% amongst matric candidates nationally.”
- Placement into post-school opportunities
- More than half of respondents who had matriculated whilst participating in Ikamva after matriculating (58% of the 119 such respondents in the survey) indicated that they had gone onto university studies, and another 14% that they had continued onto “college” (here interpreted fairly broadly as other post-school studies). This thus left only 28% who had not gone on to further studies.
Key recommendations which we’re currently considering carefully include:
- Find ways to support learners as they adjust to life at tertiary
- “Ikamva could, and should, find ways of assisting students to make the transition to university, both by assistance with the initial exposure to academic English that many respondents to the qualitative interviews found daunting, and by helping them to find support structures to reduce the anomy that they experience when starting at university. Ikamva would have to decide how much of this it wants to engage in itself (which is not its core activity), and how much can be done by assisting Ikamvanites to link to other institutions (e.g. NGOs and university structures) that could assist.”
- Provide more support to build proficiency in Academic English
- Scale cautiously:
-
“Given how important Ikamva’s leadership is in its success, one may well argue that it would be extremely difficult to scale up the activities, particularly across many more centres. The evaluation team has indeed expressed its reservations about that in previous interaction with Ikamva: It is easy for leadership to under-estimate the importance of its own role. A dilution of this leadership across a much bigger organisation may lead to the programme losing some its attractiveness to students. On the other hand, analysis shows little difference in performance between branches. This could be interpreted as that the success lies in the model, and not in the particular leadership at branch level. This would be consistent with a view that expansion could be attempted as long as good branch leadership can be found. A cautious approach may be to consider expansion only when there are good support structures and where good branch managers are available, but not to be over-ambitious. The strong central leadership capacity that Ikamva possesses for planning and organisation is an asset that could be built on and that may offer a solid foundation for expansion, but it should not be endangered by too rapid expansion. Also, expansion should retain the essentials of the existing model, which importantly includes proximity to a university environment, preferably in a metropolitan area. This limits scalability, but such a conservative stance may be appropriate.”
IkamvaYouth is greatly appreciative to the Evaluation team (Nic Spaull, Ronelle Burger, Cobus Burger, Chris van Wyk, Servaas van der Berg, Robert Dzivakwi and the fieldworkers), ikamvanite Phillip Mcelu for tracking down 95% of all ikamvanites (!), DGMT for making this possible, and to all the ikamvanites who participated in the survey and interviews.


 Lloyd Lungu
Lloyd Lungu